Week 11- Geocoding
Purpose: Create an address locator, conduct geocoding via address matching, conduct a route analysis using the Network Analyst extension, and analyze data in a model using ModelBuilder.
It may not sound like much, but this lab was heavy in content to communicate. I have been curious about how professionals apply GIS to day to day utilities and managed to get a brief glimpse of what's involved. It also served to comprehend just how critical it is for the GIS technician or cartographer to provide the most accurate and up to date data possible.
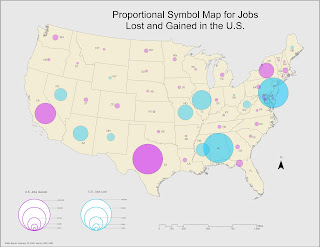
For this main exercise, we had to geocode 21 Emegency Medical Services locations within Lake County, Florida. Some sites had no matching addresses which had to be researched using the LakeEMS.org site and Bing maps in order to place them on the map correctly. In addition to mapping EMS locations, we had to select 3 random sites and find the most optimal route. The map below shows my results.
It may not sound like much, but this lab was heavy in content to communicate. I have been curious about how professionals apply GIS to day to day utilities and managed to get a brief glimpse of what's involved. It also served to comprehend just how critical it is for the GIS technician or cartographer to provide the most accurate and up to date data possible.
For this main exercise, we had to geocode 21 Emegency Medical Services locations within Lake County, Florida. Some sites had no matching addresses which had to be researched using the LakeEMS.org site and Bing maps in order to place them on the map correctly. In addition to mapping EMS locations, we had to select 3 random sites and find the most optimal route. The map below shows my results.
The second part of this lab required to explore a model in ModelBuilder. I learned what each element in the diagram below signifies, how to modify them, the role of specific tools, and how to run the model to see results in ArcMap. This particular example served to identify gas leak areas in schools.



Comments
Post a Comment