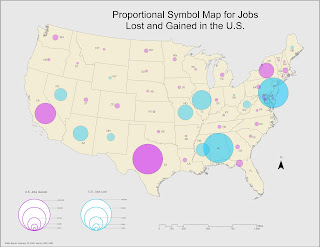
GIS5935 Week 8-- Surface Interpolation
Interpolation is utilized in order to give a raster cell a predicted number value. We use interpolation methods to create a value for unknown values basically. This is necessary for a number of different data gathering issues such as difficult environments or complex point data that could otherwise prove difficult to measure in person.
We had the opportunity to examine and perform many types of spatial interpolations in this lab such as:
- Thiessen
- Inverse Distance Weighted
- Spline
Below is the result for Thiessen. The darker polygons represent a lower BOD concentration, while white polygons represent a high concentration.
This example represents Inverse Distance Weighted interpolation. The ranges here vary from light pink, high BOD concentration, to dark green, lower BOD concentration areas.
This was a great exercise in learning how to perform each surface interpolation, actually see what makes each one unique, and get a much better idea of what type of scenarios they're better suited for.



Comments
Post a Comment